
Currently, according to medical statistics, almost all people over 25-30 years old complain of symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis. The disease affects this part of the spine more often than others. The pathology is a progressive degenerative process that affects the intervertebral discs and vertebrae located in the neck. The disease is equally common among men and women.
This is a dangerous and complex form of osteochondrosis, as there are large blood vessels in the neck that supply the brain and a large number of nerve endings. Disorders of innervation and blood flow lead to a deterioration in the supply of oxygen and nutrients to the brain.
Disease Signs
The symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis are more pronounced than in other parts of the spinal column, even with minor injuries. This is due to the fact that the vertebrae in the neck are located close to each other, and the intervertebral discs have a low height. This anatomical feature contributes to the fact that with osteochondrosis, nerve endings, the spinal cord, and blood vessels are more often compressed.
General symptoms:
- pain syndrome;
- weakness and decreased sensitivity in the upper limbs;
- restriction of neck mobility;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- frequent dizziness;
- general weakness;
- deterioration of the functioning of the organs of perception (hearing, vision, touch, taste).
Pain is often localized in the neck, radiating to the back of the head, shoulders, arms. The upper limbs hurt if the nerve root responsible for their innervation is pinched by the damaged vertebra. Pain in the back of the head is caused by spastic contractions of the neck muscles attached to the occipital bones, and impaired blood circulation in this area.
Weakness of the arms is observed in patients if a nerve root is involved in the pathological process, which provides innervation to the muscle structures of the upper extremities.
Limited mobility and a characteristic crunch when turning or tilting the neck occur if bone growths appear on the cervical vertebrae, the height of the intervertebral discs decreases, and the joints located between the vertebrae are affected.
The vertebrae in the neck have transverse processes that form a canal in which an artery that feeds the brain runs. With osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, the vertebrae are displaced, connective tissue grows on them. This leads to compression of the cervical artery, deterioration of blood supply to the cerebellum and posterior parts of the brain. As a result, a person has frequent dizziness, impaired coordination of movements, and general weakness. In advanced cases, if the artery is involved in a pathological process or is strongly pinched, then the blood supply to the cerebellum, occipital part and brain stem deteriorates significantly. In this case, the functionality of the organs of hearing, vision decreases, numbness of the tongue and fingers is observed.
The symptoms of the disease also depend on which of the eight vertebrae is affected by a degenerative or inflammatory process. Disorders of sensitivity and movement are caused by damage to the spinal roots, which are affected by certain vertebrae. Depending on this, the following manifestations of cervical osteochondrosis are observed:
- first vertebra - the neck and occipital part of the head grow numb, their sensitivity decreases;
- second - there is soreness in the region of the crown and occiput;
- third - soreness is felt and sensitivity decreases in the part of the neck where the compressed spinal root is located, the intensity of taste sensations decreases, speech disorders are present;
- fourth - painful sensations radiate to the shoulder, scapula, the patient is worried about cardiac pains, breathing disorders, the tone of the neck muscles decreases;
- fifth - pain is noted in the neck, given to the outer surface of the shoulder;
- sixth - pain in the neck radiating to the scapula, felt in the forearm and thumbs;
- seventh - pain is given to the scapula, back of the shoulder, forearm and fingers (from the second to the fourth);
- eighth - pain spreads from the neck to the shoulders, forearms and little fingers.
There are four degrees of cervical osteochondrosis, depending on the extent of the lesion. These are not the stages of the disease, but the severity of the symptoms, due to how widespread the pathological process is, which vertebrae it affects.
- At first degree, clinical symptoms are absent or minimal. Patients complain of mild pain, aggravated by head movements. Treatment initiated at this stage of the disease will be effective. However, people often ignore the alarming symptoms or do not feel them, so they do not go to the doctor.
- Aggravation of the pathological process increases the symptoms. In the second stage, the pain becomes more pronounced, is given to the upper limbs, shoulder blades. At this stage of the development of the degenerative process, the height of the intervertebral disc decreases, as a result of which the nerve fiber is pinched. This becomes the cause of increasing pain. For the second degree of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, headaches, deterioration of health, and decreased performance are characteristic.
- The third degree of cervical osteochondrosis is characterized by the formation of a hernia of the affected intervertebral disc. Neck mobility is limited; on palpation, the patient feels severe pain. With such a spread of the pathological process, pain becomes constant, radiating to the upper limbs. There is a feeling of tension in the muscles attached to the occipital bones. Patients complain of frequent dizziness, general weakness, numbness of the hands.
- The fourth degree of cervical osteochondrosis is diagnosed when the intervertebral disc is completely destroyed by the degenerative process. It is replaced by fibrous tissue, which leads to a significant restriction of mobility. The spinal cord and the blood vessels in the neck are affected. Such changes are characterized by a significant deterioration in the blood supply to the cerebellum and the occipital part of the brain. Oxygen starvation leads to impaired coordination of movements, impairment of hearing, vision, numbness of the tongue, and speech disorders.
Treatment methods
A timely visit to a doctor when the first alarming symptoms, discomfort in the neck, reactions from the nervous system appear will prevent the progression of degenerative changes. Treatment of cervical osteochondrosis consists of a set of therapeutic measures. Among them:
- taking medications;
- massage;
- physiotherapy exercises;
- physiotherapy procedures.
Treatment is carried out at home and on an outpatient basis, under the supervision of a doctor. In some cases, more radical methods may be required, then the patient is hospitalized.
Drug therapy
The following groups of drugs are used to treat osteochondrosis of the cervical spine:
- anti-inflammatory nonsteroidal drugs;
- chondroprotectors;
- muscle relaxants;
- drugs that improve blood rheological parameters;
- B vitamins
Doctors prescribe anti-inflammatory drugs to reduce the intensity of pain, reduce inflammation and swelling of the nerve root. Chondroprotectors restore damaged cartilage tissue in the intervertebral disc. Muscle relaxants relax the neck muscles, relieve spasms. Medicines to improve blood flow help restore the impaired blood supply to the brain. B vitamins activate metabolism in nerve tissues. With intense pain, the doctor may prescribe analgesic drugs. If the patient has severe pain syndrome, then analgesics are administered parenterally, after the pain subsides, they switch to pills.
In addition to pharmaceutical medications, the patient can use traditional methods of treating cervical osteochondrosis. Before using them, you need to consult a doctor so that there is no conflict between medicines and non-traditional means. Decoctions and infusions from dill seeds, hop cones, lilac flowers help to stop the inflammatory process and relieve pain.
Physiotherapy
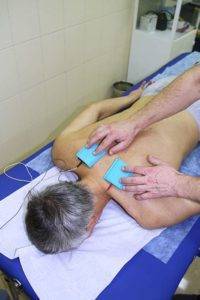
Physiotherapy is an effective way to combat osteochondrosis of the cervical spine. It is imperative to treat this disease using such techniques, as a result of which the following results are achieved:
- pain intensity decreases;
- activation of the restoration of the affected bone, cartilage and muscle tissues;
- muscle spasm and tension are relieved;
- the inflammatory process is stopped;
- improves the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to the affected area and the brain.
The following types of procedures are considered the most effective in the treatment of osteochondrosis:
- drug electrophoresis (an electric current is applied to the affected area, which, in addition to activating blood flow and tissue restoration, improves the delivery of the active substance of the drug to the tissues affected by the degenerative process);
- ultrasound therapy (metabolic processes in the diseased area are activated, soreness decreases, inflammation is stopped);
- magnetotherapy (relieves swelling from the affected area, which helps to reduce the intensity of pain);
- laser therapy (improves blood circulation in the area of the pathological process, has an anti-inflammatory effect).
Also the doctor can advise acupuncture, balneological procedures.
Physiotherapy exercises
Exercises are prescribed during the period when acute manifestations of the disease are stopped. During gymnastics, there should be no discomfort and soreness.

The complex should be performed upon reaching a stable remission to prevent relapses.
- Take a prone position, raise your head and body, leaning on your hands. The back is straight, breathing is deep and even. Hold in position for a minute or two, then slowly take the starting position. The number of repetitions is 3.
- Position - lying on your stomach, arms along the body. Slowly turn your head, trying to touch your ear to the floor. Repeat 6 times on each side.
- Sitting or standing, tilt your head while inhaling, trying to reach your chest with your chin. As you exhale, gently pull your head back, raising your eyes to the ceiling. The number of repetitions is 10-15.
- A good exercise to strengthen your neck muscles is to press your forehead onto your hands. To achieve the effect, you need to press with your palms on your forehead and your forehead on your palms for 30 seconds. Repeat three times.
- Rotate your head in a circle. The exercise should be done slowly, smoothly. In each direction - 10 turns. The occurrence of dizziness when performing movements is unacceptable. If this happens, you should stop immediately.
All exercises must be done smoothly, without sudden movements, in case of deterioration of health, the appearance of nausea, dizziness, stop immediately.
Massage
The course is prescribed by the doctor in the absence of acute pain, it can only be carried out by a specialist with medical education. With such a disease, it is not recommended to contact non-professionals.
Neck Massage Healing Effects:
- improves blood and lymph flow in the affected area;
- muscles relax, spasm relieves;
- the intensity of painful sensations decreases.
Specialists use the entire arsenal of massage movements: stroking, rubbing, kneading, squeezing and vibration.
Surgery
The operation is indicated if conservative therapy does not bring results within six months, the patient suffers from severe pain, signs of nerve fiber damage and myelopathy are observed. If osteochondrosis of the cervical spine proceeds with complications, there is a threat of stroke, there is a strong compression of the spinal cord, then an operation is necessary.
According to indications, the following types of surgical interventions are used:
- endoscopic discectomy - removal of part or a whole intervertebral disc;
- laminotomy - excision of bone ligaments and overgrown particles of bone tissue (often combined with laminoplasty - the installation of artificial plates to expand the spinal canal);
- laser vaporization of the disc nucleus - splitting the nucleus of the intervertebral disc with a laser beam simultaneously with the destruction of its destroyed fragments;
- cold plasma nucleoplasty - instead of an endoscope, a long and thin hollow needle is used, which is inserted into the intervertebral disc, through which an electrode is delivered to the lesion site, which has a cold plasma effect.

The neck is a complex organ containing large blood vessels, the spinal cord. They are easy to damage, so surgical interventions are resorted to in no more than 5% of cases. Surgical treatment is often accompanied by the development of complications. Among them:
- inflammatory process in the tissues or membranes of the spinal cord;
- osteomyelitis;
- scarring resulting in narrowing of the arterial and spinal canals.
Surgery on the cervical spine is difficult and requires a long rehabilitation period. The recovery of a patient after surgery takes six months or more.
Prevention
To prevent the development of cervical osteochondrosis it is necessary:
- monitor the position of the spine and neck;
- lead an active lifestyle, move more;
- while doing physical exercises, one must be careful, observe the correct execution, since even minor injuries can affect the condition of the musculoskeletal system;
- take care of the correct body position during sleep, purchase an orthopedic or anatomical mattress;
- to properly equip a workplace where a person spends a lot of time;
- regularly engage in physical education;
- monitor the diet, ensure the supply of all the useful minerals necessary for strong bones, especially magnesium and calcium;
- constantly undergo dispensary examinations for the timely detection of osteochondrosis.
Prevention will help prevent degenerative changes in the cervical spine, protect against painful sensations, dizziness, numbness of the limbs and other unpleasant symptoms.





































